polarimeter basic principle|polarimeter parts and functions : commercial In this article, we will explore how a polarimeter works and its various applications in different fields. How Does a Polarimeter Work? A polarimeter works on the principle of . web9 de mai. de 2023 · Phoenix. Phoenix is not only a mythical being, but also a constellation seen in the southern sky. In 2023, Paris Hilton named her baby boy Phoenix which may cause it to trend upward for both boys and girls. .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Supercell ID is a brand new service that safeguards your games across devices. See what it’s all about: How to Get Started? . It takes about a minute or two — you don’t even need a password! Watch the Tutorial. Watch our Getting Started tutorial for more information! Supercell ID - Getting .
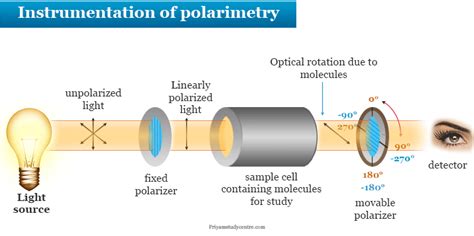
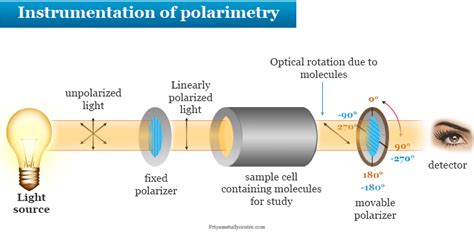
The basic operation principle of a polarimeter comprises the following: One generates light with an accurately prepared linear polarization state, usually by passage through a polarizer. That light is sent through the optically active .A polarimeter is an instrument which measures the angle of rotation by passing polarized light through an optically active (chiral) substance. To measure optical rotation, a Light Emitting Diode (LED) produces a beam of ordinary light.
A polarimeter is an instrument used to determine the angle through which plane-polarized light has been rotated by a given sample. You will have the opportunity to use a polarimeter . Principles of Polarimetry. Polarimetry measures the rotation of polarized light as it passes through an optically active fluid. The measured rotation can be used to calculate the . In this article, we will explore how a polarimeter works and its various applications in different fields. How Does a Polarimeter Work? A polarimeter works on the principle of .
This guide will cover the basic principles of polarimetry, including the different types of polarimeters and how they work. It will also provide practical guidance on how to use polarimeters effectively, including tips for sample preparation and . In a polarimeter (figure 2), plane-polarized light is introduced to a tube (typically 10 cm in length, figure 3) containing a solution with the substance to be measured. If the substance is optical inactive, the plane of the polarized light .
Principle of polarimetry. Polarised light is light that has passed through a ‘polariser’, which forces the randomised electromagnetic waveforms into one plane.
Polarimetry is the measurement of the polarization state of light. It can be used to measure the polarizing properties of materials, optical components and systems such as . By understanding the basic principles of how a polarimeter works, following the step-by-step process, and avoiding common pitfalls, users can achieve accurate and consistent results. Proper maintenance and care will also extend the life and reliability of the instrument, ensuring long-term success in all applications. Principles of Polarimetry. Polarimetry measures the rotation of polarized light as it passes through an optically active fluid. The measured rotation can be used to calculate the value of solution concentrations; especially substances such as sugars, peptides and volatile oils. A polarimeter consists of a polarized light source, an analyzer, a graduated circle to measure .
Since a polarimeter measures the refraction, or bending of light through a medium, they are largely chemistry and physics instruments. The samples used to measure the effect must be partially transparent. They have .
A polarimeter works on the principle of optical rotation, which is the rotation of the plane of polarization of light as it passes through certain materials. . Polarimeter Spectrometer: This type of polarimeter is used to measure the optical activity of a sample over a wide range of wavelengths. It is commonly used in physics and chemistry . Polarimeter is a basic measuring instrument in optical communications, polarization imaging and other related applications. In this paper, we will review the progress in polarimeters in recent years. Firstly, the basic principle of polarization and the methods for polarimeters are introduced.Optical Rotation (Optical Activity) - When a beam of plane-polarized light propagates through a quartz crystal along the optic axis, the plane of polarization steadily turns about the direction of the beam. Learn more about Optical rotation, Specific rotation, formula and its applications at . Polarimeter - Download as a PDF or view online for free. . Although most manual polarimeters produced today still adopt this basic principle, the many developments applied to the original opto-mechanical design over the years have significantly improved measurement performance. The introduction of a half-wave plate increased "distinction .
By reducing the path length of the sample cell from 100 mm to e.g. 2.5 mm or reducing the concentration of the sample, the result will be compatible with the measuring range of the polarimeter. In order to determine the specific rotation of a substance, the MCP polarimeter can use a shorter sample cell than 100 mm.
Polarization is a basic property of light and is fundamentally linked to the internal geometry of a source of radiation. Polarimetry complements photometric, spectroscopic, and imaging analyses of .The basic spectrophotometer instrument consists of a light source, a digital display, a monochromator, a wavelength sector to transmit a selected wavelength, a collimator for straight light beam transmission, photoelectric detector and a cuvette to place a sample. The intensity of light is symbolized as l 0 measure the number of photons per . Fluorimetry Principle. Fluorimetry is based on the principle of emission of light by a substance after the absorption of light of a specific wavelength. . Basic Microbiology (63) Biochemical Test (114) Biochemistry (164) Bioinformatics (22) Biology (212) Biotechnology (34) Cell Biology (107) Culture Media (67)
This lesson demonstrates how polarizers work to detect chiral molecules in solution.
A polarimeter refers to an optical instrument used to determine the polarization properties of light beams and samples. It consists of a polarization generator and analyzer, which produce and analyze a beam of known polarization state. . followed by a hybrid coupler and then the detectors. Although more complicated in principle, such a .
Based on his research, he designed one of the first polariscopes, and formulated the basic quantitative laws of polarimetry. In 1850, Wilhelmy used polarimetry to study the reaction rate of the hydrolysis of sucrose. In 1874, van't Hoff proposed that a tetrahedral environment of the carbon atom could explain the phenomenon of optical activity .Rudolph Research Analytical 55 Newburgh Road Hackettstown, NJ, 07840 USA Phone: 973-584-1558 Fax: 973-584-5440 [email protected]’s more, if your needs change, our digital polarimeter changes with you. With their multiwavelength options, you can easily adapt them for future needs. Fast measurement results are delivered in seconds, and the broad portfolio .
Principle of Colorimeter. When an incident light beam with intensity I 0 passes through a solution, a part of the incident light is reflected (I r) and absorbed (I a) while the remaining incident light is transmitted (I t).. i.e., I . A polarimeter is an instrument that measures the optical rotation of a substance. Optical rotation is the property of a substance to rotate the . They are typically used for educational purposes or for basic analytical work. Manual polarimeters require the user to manually measure the optical rotation of a substance using a graduated circle . Polarimeter is a basic measuring instrument in optical communications, polarization imaging and other related applications. In this paper, we will review the progress in polarimeters in recent years. Firstly, the basic principle of polarization and the methods for polarimeters are introduced.
An easily constructed and inexpensive polarimeter with an optical rotation angle resolution of about 0.5° is presented. It is made from small pieces of polarizing film, 2 LEDs, a protractor, and .A polarimeter is a device used to measure the rotation of plane polarized light caused by optically active compounds in a solution, such as in the determination of sucrose and reducing sugars in fruit and fruit products. . by different magnetographs and Stokes polarimeters at different observatories are important for understanding the basic .Basic Principles of Raman Scattering and Spectroscopy. Authors: Chase Toncheff,Emily Bishop Raman scattering is a physical process in which the direction, and more importantly, the energy of incoming light changes as it scatters off of a sample. Light that interacts with a sample can experience one of a few different phenomena; most of the .
why polarimeter is used
The operation of the refractometer is based on the physical principle of light refraction – Snell’s law – which is further described in the next chapter. Light slows down as it passes into more optically dense media, and speeds up as it passes into less optically dense media. . Necessary cookies enable the basic functioning of the .
POLARIMETER TUBE, STAINL. STEEL, 10 mm TOOLMASTER WL, LÜR, VOL. 0.2 ml . Compatible with: . Necessary cookies enable the basic functioning of the website. Show cookie information Hide cookie information Marketing (0) Marketing cookies are used by third parties or publishers to show you personalized advertising. .• Basic principles - Resonance Raman scattering - Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) • Instrumentation -Spectrometer - Excitation sources • Raman in catalysis - In situ cells - In situ Raman (of working catalysts) C. Hess, 2006Synthetic aperture radar image of Death Valley colored using polarimetry.. Polarimetry is the measurement and interpretation of the polarization of transverse waves, most notably electromagnetic waves, such as radio or light waves.Typically polarimetry is done on electromagnetic waves that have traveled through or have been reflected, refracted or .
Principle: Polarography is based upon the principle that gradually increasing voltage is applied between two electrodes, one of which is polarisable (dropping mercury electrode) and other is non-polarisable and current flowing between the two electrodes is recorded. A sigmoid shape current-voltage curve is obtained
bottle-brush test
bottle-point adsorption test
webOUR MOST POWERFUL, PLANT-POWERED MULTIVITAMIN – With 12 essential vitamins, 10 essential minerals and 22 nutrients from colorful fruits, vegetables and herbs packed into every tablet, Nutrilite™ Double X™ is .
polarimeter basic principle|polarimeter parts and functions